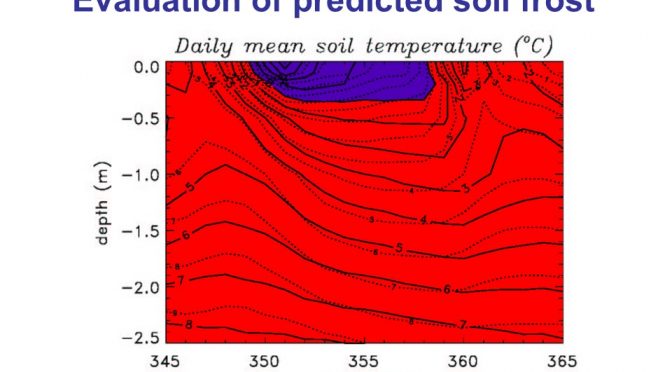
Modeling of soil processes including groundwater recharge, frozen ground and permafrost
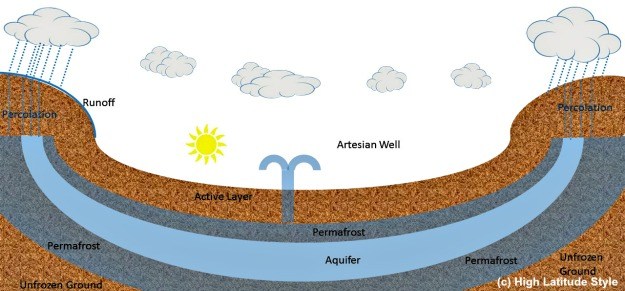
This unit expands the concepts of the soil-air-water composite by the inclusion of ice. Frozen ground and permafrost affect the water uptake and hence there existence has impacts on infiltration, runoff and ground water formation and evapotranspiration.
Goals
The goal of this unit is to cover the fate of water in frozen ground and permafrost, freezing and thawing of the active layer that permits vegetation to grow, and the consequences of frozen ground and permafrost for water uptake by soil and ground water recharge, respectively.
After successful completion of this unit students will be able to
- Explain permafrost and active layer
- Describe the interaction of the energy and water budget in the ground
- Determine soil ice content for various soils
Students’ tasks
- Read page 51 to 70 of chapter 2 in New Permafrost and Glacier Research
- Take notes and fill out the questionnaire prior to Thursday 2359 Alaska time
- Solve the tasks assigned at your class level in this Unit 13 Applications sheet and submit the scanned solution by Thursday 2359 Alaska time
Supplemental material
Example of a worked problem on frozen ground
© 2019 Nicole Mölders | All rights reserved